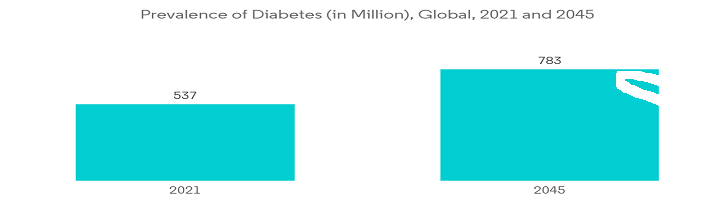We are thrilled to extend a warm invitation to scientists, doctors, endocrinologists, dieticians, and scholars for the "8th International Conference on Diabetes and Cholesterol Metabolism," scheduled from November 28-29, 2024, in Chicago, USA. Our conference, themed "Global trends and statistics in diabetes and cholesterol-related diseases" aims to shed light on recent advancements in diabetes and cholesterol metabolism, fostering knowledge sharing among experts and empowering the next generation of scholars and researchers in this field.
The scientific sessions will delve into various aspects including diabetes mellitus, complications, endocrinology, obesity, metabolic syndrome, epidemiology, cholesterol and lipid metabolism, cardiovascular diseases, hypercholesterolemia, as well as recent advances in treatments and therapies.
We cordially invite delegates from around the globe, including scholars, researchers, students, and industrial representatives, to join us at this enlightening event. Our conference is open to diverse research methodologies, offering a platform to explore new dimensions in diabetes and metabolic diseases.
Target Audience:
-
Endocrinologists
-
Diabetologists
-
Physicians
-
Researchers
-
Scientists
-
Diabetes Societies and Associations
-
Dietitians
-
Epidemiologists
-
Business and Academic Professionals
-
Students
-
Medical and Pharmaceutical Companies
Benefits of Attending:
-
Exchange knowledge and network with leading experts in endocrinology, diabetology, and metabolic syndrome.
-
Discuss strategies to combat metabolic syndrome and diabetes.
-
Explore innovative ideas applicable to practice.
-
Engage with fresh minds to broaden perspectives on diabetes and metabolic diseases.
-
Learn about key developments and challenges from esteemed speakers.
-
Experience a comprehensive agenda featuring presentations, panel discussions, roundtables, and workshops covering a range of topics.
-
We eagerly anticipate your participation in November 28-29, 2024, in Chicago, USA as we collectively strive to advance our understanding and management of diabetes and cholesterol metabolism.
Track 01: Diabetes: Internal Medicine and Primary Care
Internists specialize in treating complex adult medical conditions, including heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, and chronic lung disease. They provide comprehensive care in hospital and outpatient settings, and also engage in teaching and research.
Primary care providers serve as the first point of contact for patients in the healthcare system, offering comprehensive care and focusing on preventive measures. They diagnose and monitor conditions like diabetes, working to improve public health by ensuring access to medical services.
-
Diagnosing diabetes
-
Monitoring diabetes
Track 02: Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a metabolic condition marked by high blood sugar levels. Insulin, responsible for transferring sugar from the bloodstream into cells for energy or storage, is either insufficiently produced or not effectively utilized by the body in diabetes. Symptoms of diabetes are linked to elevated blood sugar levels, facilitating straightforward diagnosis in most cases. The primary goal of diabetes management is to enhance the quality of life and productivity of individuals with diabetes.
Key aspects of diabetes management include education on:
-
Differentiating between type 1 and type 2 diabetes
-
Gestational diabetes
-
Identifying risk factors and symptoms
-
Monitoring blood sugar levels through random and fasting tests
-
Implementing dietary and physical activity measures
-
Utilizing medication for diabetes management
Track 03: Clinical Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus encompasses a spectrum of conditions marked by abnormal glucose tolerance. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), or type 1 diabetes, necessitates external insulin for management and was previously termed juvenile-onset diabetes. It affects around 10% of all diabetics. Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), or type 2 diabetes, often referred to as adult-onset or maturity-onset diabetes, typically develops gradually with hyperglycemia, posing minimal risk of ketoacidosis except in severe stress situations. Clinical research in diabetes encompasses studies on the causes, mechanisms, prevention, and treatment, including medical and self-management approaches, for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes across all age groups.
Track 04: Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes, affecting up to 10% of pregnant women annually, elevates blood sugar levels during pregnancy. It's divided into two classes: A1 managed by diet and exercise, and A2 requiring insulin or medication. Unlike type 1 diabetes, it develops late in pregnancy, reducing birth defect risks. Complications like macrosomia and hypoglycemia are controllable through strict blood sugar management upon diagnosis. Early detection and preventive measures are vital in managing gestational diabetes.
-
Macrosomia
-
Hypoglycemia
-
Types of gestational diabetes
-
GD and Birth defects
Track 05: Pediatric Diabetes and Endocrinology
Hyperglycemia in diabetes mellitus results from insufficient insulin (type 1) or insulin resistance (type 2). Children primarily develop type 1 diabetes, which mirrors adult cases. The endocrine system, comprising ductless glands, releases hormones directly into the bloodstream. Endocrinology investigates hormone functions and disorders.
-
Endocrine Glands and Hormones
-
Hormone Metabolism
-
Hormonal Receptors
-
Signaling Mechanisms
-
Hormone Regulated Gene Expression
-
Pediatric Endocrinology
Track 06: Diabetes Etiology
In medicine, etiology identifies disease causes. From the germ theory to modern insights, it's crucial for understanding disease origins. Diabetes has both disease-specific and individual-specific causes, involving genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Type 1 diabetes results from immune system attacks on pancreatic cells, while type 2 involves insulin resistance and genetic factors. Aging, inactivity, and obesity worsen insulin resistance.
-
Environmental factors
-
Genetic factors
-
Lifestyle factors/demographics
-
Disease associated with diabetes
Track 07: Epidemiology of Diabetes
Epidemiology investigates the frequency and reasons behind disease occurrences in different populations. This data informs the development and evaluation of disease prevention programs and treatment strategies. With diabetes prevalence escalating globally due to rising obesity rates and unhealthy lifestyles, understanding its epidemiology is crucial. Key categories in diabetes epidemiology include population trends, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, age and gender disparities, ethnic variations, and diabetes-related morbidity and mortality.
-
Diabetes and age
-
Diabetes and gender
-
Diabetes and ethnic background
Track 08: Pathogenesis of Diabetes
Pathogenesis refers to the process by which a condition or disease develops, encompassing factors contributing to its onset, progression, and maintenance. In diabetes mellitus, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, pathogenesis involves either insufficient insulin secretion or a combination of insulin resistance and inadequate insulin production. Type 1 diabetes, commonly seen in both children and adults, results from the immune system's attack on pancreatic beta cells responsible for insulin production. Conversely, insulin resistance is a primary metabolic abnormality leading to the development of type 2 diabetes. This condition arises from a series of pathophysiologic changes, each posing a risk to normal glucose regulation.
Track 09: Epigenetics and Epigenomics of Diabetes
Epigenetics investigates cellular influence on gene activity without DNA sequence changes, while epigenomics explores broader alterations in gene control. These changes are linked to conditions like prediabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance.
Diabetes, a metabolic disorder, results from genetic and environmental factors. Its global prevalence raises treatment costs and complications. The disease is attributed to genetic predisposition and significant gene alterations.
-
Epigenetic Reprogramming
-
Epigenetic Variation
-
Epigenetic Signals
Track10: Physiology and Pathophysiology of Diabetes
Physiology studies organismal processes, including disease complexities involving multiple organs and tissues. In diabetes, insulin levels and utilization are pivotal. Type 1 lacks insulin, while type 2 involves peripheral insulin resistance. Diabetes pathophysiology, influenced by various hormones like insulin and glucagon, is intricate, with liver and renal involvement, presenting diverse patient variations.
-
Managing diabetes
-
Diabetes and Oxidative Stress
Track 11: Global Diabetes Market
The diabetes market has significantly matured in the past two decades due to increased innovation and modern therapeutic treatments. With the condition's prevalence and patient numbers expected to rise, it has become a lucrative market for drug developers. According to Global Data, a leading data and analytics organization, the global pharmaceutical sales related to diabetes have expanded sixfold since 2000. Additionally, the market for diabetes monitoring devices is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5%, reaching $27.0 billion by 2025 from $19.7 billion in 2020.
Track 12: Diabetes Research and Case Reports
Diabetes results from insufficient insulin production or its ineffective use, causing symptoms like frequent urination and increased thirst. Clinical case reports, documenting unique patient cases, are vital for sharing new clinical insights and require patient consent and privacy considerations.
-
Global Market for Diabetes Monitoring Devices
-
Analysis of Global Market Trends
-
Regulatory and Economic Trends Affecting the Market
Analysis of the Endocrinology Drugs Market
Anticipated growth in the endocrinology drugs market is projected at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period from 2022 to 2027.
Segmentation of the Endocrinology Drugs Industry
In accordance with the report's scope, endocrinology pertains to the field of physiology and medicine focusing on hormones and endocrine glands. Drugs addressing disorders of these glands fall under the category of endocrinology drugs. The Endocrinology Drugs Market is categorized by Therapy Area (Adrenal Insufficiency, Diabetes, Thyroid Hormone Disorder, and Other Therapy Areas), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies), and Geographic Regions (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East, Africa, and South America). The report also provides insights into market sizes and trends across 17 different countries in key global regions.
Endocrinology Drugs Market Trends
Diabetes Expected to Lead the Market in the Forecast Period
Diabetes ranks as the most prevalent endocrine disorder in the United States. According to data from the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the number of people with diabetes increased from 34.2 million in 2018 to 37.3 million in 2020. The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) reported in November 2021 that 1 in 6 adults worldwide lives with diabetes, with nearly half of those with diabetes in Mexico remaining undiagnosed. In the North America and Caribbean region, 1 in 7 adults (51 million) are affected by diabetes, according to the same source.
Moreover, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's 2021 updates indicate that new diabetes cases among U.S. adults aged 18 years and older numbered 1.4 million in 2019. Among adults aged 45 and older, the incidence of diagnosed diabetes increased significantly compared to those aged 18 to 44 years. This notable rise in new cases with age, particularly between 45 and 64 years, is expected to drive the demand for endocrinology drugs throughout the forecast period.
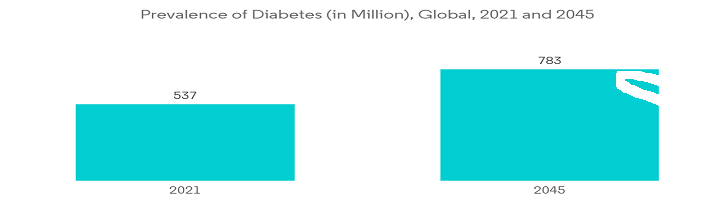
North America's Expected Market Dominance in the Forecast Period
North America is projected to hold a significant market share due to its robust healthcare infrastructure, high rates of obesity, unhealthy dietary habits, changing lifestyles, and continuous introduction of new products. For instance, in August 2021, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved the rapid-acting insulin Lyumjev (insulin lispro-aabc injection) 100 units/mL, indicated to enhance glycemic control in adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, the approval of the first interchangeable biosimilar insulin product, Semglee (insulin glargine-yfgn), was granted by the United States Food and Drug Administration in July 2021.
These approvals are expected to bolster growth in the endocrinology drug market. Furthermore, Rybelsus received Health Canada's approval in April 2020 for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults. Considering these factors, North America is poised to maintain its dominance in the endocrinology drugs market throughout the forecast period.