Theme: Be stronger than Diabetes
Metabolic Diseases 2018
ME Conferences takes the immense pleasure for inviting the scientists, doctors, endocrinologists, dieticians and scholars to the “International Conference on Diabetes and Cholesterol Metabolism” which is going to be held on October 15-17, 2018 at Dubai, UAE. The upcoming conference will be organized around the theme "Be Stronger than Diabetes".
The International conference enlightens the recent advancements related to Diabetes, cholesterol metabolism and aims on sharing the knowledge of the expertise in this field where the new generation scholars and researchers can increase their knowledge related to diabetes and metabolic diseases. The scientific sessions emphasize on diabetes mellitus, diabetes complications, endocrinology, obesity, metabolic syndrome, epidemiology of diabetes, cholesterol metabolism, lipid metabolism, cardiovascular diseases, hypercholesterolemia, recent advances in treatments and therapies.
ME Conferences welcome the delegates across the globe to enlighten the young and fresh minds of the scholars, researchers, student communities and industrial delegates to attend the “International Conference on Diabetes and Cholesterol Metabolism’’ as it is open to research methodologies which explores the new dimensions regarding this field.
Target Audience:
-
Endocrinologists
-
Diabetologists
-
Doctors
-
Physicians
-
Researchers
-
Scientists
-
Diabetes Societies and Associations
-
Dietitians
-
Epidemiologists
-
Business Professionals
-
Academic Professionals
-
Students
-
Medical & Pharmacy Companies
Benefits of Attending:
- Exchange knowledge and network with leading Endocrinologists, Diabetologists, Metabolic Syndrome experts, Metabolism professionals, Clinicians, Metabolic Syndrome and Nursing Care specialists and foundation leaders.
- Discuss approaches to overcome Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes.
- Discuss quality ideas that can be applied in the practice.
- Fresh minds will have the opportunity to explore more areas of expertise on Diabetes and Metabolic Diseases.
- Learn and discuss key news and challenges with senior level speakers.
- With presentations, panel discussions, roundtable discussions, and workshops, we cover every topic from top to bottom, from global macro issues to micro issues.
We look forward to meet you at Dubai, UAE.
Track 1: Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar (glucose) levels, either because of insulin production is inadequate or because the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin or both. Type 1 diabetes (insulin-dependent diabetes) was known as juvenile diabetes as it is usually diagnosed in children and young adults. It arises from the autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing pancreatic β cells and it can be managed with insulin as well as dietary changes and exercise. Whereas type 2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent diabetes) is a heterogeneous condition resulting from a combination of insulin resistance and inadequate insulin secretion by pancreatic beta cells. Type 2 diabetes can be managed with non-insulin medications, insulin, weight loss, or dietary changes. Type 3 diabetes is caused by the insulin resistance in the brain and it may lead to Alzheimer’s disease. There are several other rare types of diabetes such as latent autoimmune diabetes of adults (LADA), double diabetes, and brittle diabetes. The common symptoms of diabetes are weight loss, slow healing wounds, polyuria (increased urination), numbness in the feet, polydipsia (increased thirst), and polyphagia (increased hunger).
Track 2: Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes in which a woman develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Pregnancy hormones and increased fat deposits during pregnancy mediate insulin resistance during pregnancy. Pregnancy hormones compete with the insulin for the insulin receptor. Insulin resistance prevents glucose from entering the cells properly. As a result, glucose remains in the bloodstream, where glucose levels rise. It can be managed by exercise and a healthy diet. Insulin injections are the most common medical treatment for gestational diabetes. If gestational diabetes is not detected and controlled, it may increase the risk of birth complications, such as shoulder dystocia (when the baby's shoulder gets stuck during the birth). Babies of mothers with gestational diabetes may experience respiratory distress syndrome, hypoglycaemia and can also be large for their gestational age. Women with gestational diabetes are at high risk of developing diabetes mellitus later in life.
Track 3: Diabetes Complications
Several types of complications are seen due to uncontrollable diabetes. Long-term complications of diabetes develop gradually. They are divided into microvascular (due to damage to small blood vessels) and macrovascular (due to damage to larger blood vessels). Microvascular complications include damage to eyes, kidney failure and impotence. Macrovascular complications include cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks, strokes and insufficiency in blood flow to legs. The other factors that quicken the complications of diabetes include smoking, high cholesterol levels, obesity, high blood pressure, and lack of exercise. By controlling the blood sugar level and regular diabetes check-ups, risk of complications can be lowered. Early recognition and prevention of the diabetic complications are mandatory for the improvement of the quality of life and psychological outcome of these patients.
Track 4: Endocrinology
Endocrinology is the study of endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. Examples of hormones include thyroid hormone, growth hormone, and insulin. These hormones influences major body functions, including the body's ability to change calories into energy, also regulate processes, such as appetite, breathing, fluid balance, feminization, and weight control. The endocrine system also influences heart beats, bones and tissues growth. It plays a vital role in whether or not you develop diabetes, thyroid disease, growth disorders, sexual dysfunction, and a host of other hormone-related disorders.
Endocrinology diseases may relate to too much or too little secretion of a hormone, too much or too little action of a hormone, or problems with receiving the hormone. Common endocrine disorders include diabetes mellitus, Addison’s disease, Cushing’s syndrome, Graves’ disease, acromegaly, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism. These disorders often have widespread symptoms, affect multiple parts of the body, and can range in severity from mild to very severe. Treatments often relays on adjusting hormone balance using synthetic hormones. Untreated endocrine disorders can have widespread complications throughout the body.
Track 5: Diabetes and Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition which results from the accumulation of excess fat on the body. Obesity is thought to trigger changes to the body's metabolism. It also adds pressure on body's ability to use insulin, to properly control blood sugar levels, and are therefore more likely to develop diabetes. The abdominal fat influences fat cells to release ‘pro-inflammatory’ chemicals, which can reduce insulin sensitivity by disrupting the function of insulin responsive cells and their ability to respond to insulin. Obesity also causes prediabetes, a metabolic condition that almost always develops into type 2 diabetes.
Obesity has many causes such as age, gender, genes, psychological makeup, socioeconomic, and environmental factors. Certain medical conditions and medications can cause or promote obesity, although these are much less common causes of obesity than overeating and inactivity. Some examples of these are depression, certain medications (examples are steroids, antidepressants, control pills), Polycystic ovarian syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome. The goal of obesity treatment is to reach and stay at a healthy weight. All weight-loss programs focus on eating habits and physical activity.
Track 6: Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of risk factors which includes high blood pressure, hyperglycemia, abnormal cholesterol levels and excess body fat around the waist that occur together, doubling your risk of heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. This condition is also known by other names including Syndrome X, insulin resistance syndrome, and dysmetabolic syndrome. Insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and prediabetes have overlapping aspects and are closely linked to one another. Most of the disorders associated with metabolic syndrome have no symptoms, although it is closely linked to insulin resistance, overweight or obesity and inactivity. Metabolic syndrome can be prevented or reversed by adopting few number of lifestyle changes, including losing weight, regular exercise, healthy diet, stopping smoking, cutting down on alcohol. Elevated liver enzymes, an indicator of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, may comprise an additional component of the metabolic syndrome and may serve as a surrogate marker for type 2 diabetes.
Track 7: Epidemiology of Diabetes
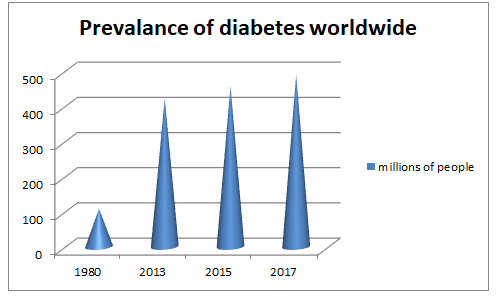
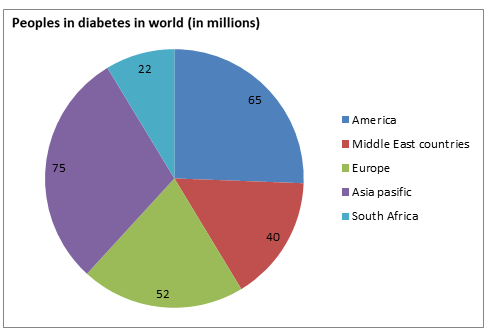
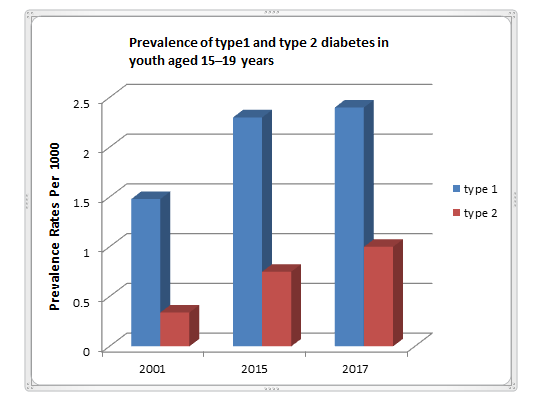
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of incidence, distribution, and possible control of diseases and other factors relating to health. As per the statistics in 2017, an estimated 8.8 % of the global adult population were living with diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes has nearly doubled since 1980, rising from 4.7% to 8.8% in the global adult population. This reflects an increase in associated risk factors such as overweight or obese. Over the past decade, diabetes prevalence has risen faster in developing countries than in developed countries. Type 2 diabetes mellitus occurs throughout the world, but is more common in the more developed countries. The disease burden related to diabetes is high and rises in every country. The premature morbidity, mortality, reduced life expectancy and financial and other costs of diabetes make it an important public health condition.
Track 8: Diabetic Education and Healthcare Professionals
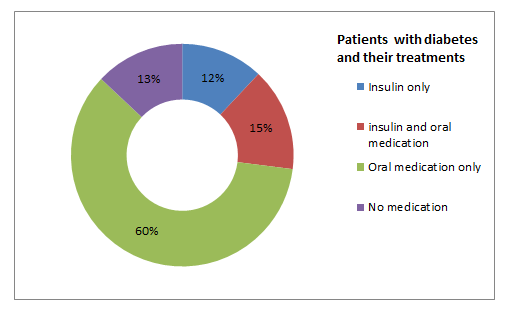
Diabetes education is an integral component of the diabetes management and care, because diabetes requires day-to-day knowledge of nutrition, exercise, monitoring, and medication. A healthy diet is central to the management of diabetes. The aim of patient education is for people with diabetes to improve their knowledge, skills and confidence, enabling them to take increasing control of their own condition and integrate effective self-management into their daily lives. High-quality structured education can have an effect on health outcomes and can significantly improve quality of life. The potential benefits of an effective patient education programme for people with diabetes should include improving knowledge, health beliefs and lifestyle changes, improving patient outcomes - eg, weight, haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), lipid levels, smoking and psychosocial changes, improving levels of physical activity, reducing the need for - and potentially better targeting of - medication and other items such as blood testing strips.
Track 9: Cholesterol, High Blood Pressure and Diabetes
Cholesterol is an organic substance that body uses to produce vitamin D, make certain hormones and build healthy cells. High cholesterol and diabetes are linked to each other. Diabetes can disturb the balance between HDL and LDL cholesterol levels. LDL particles of the people with diabetes tend to stick to arteries and can easily damage blood vessel walls. Glucose coated LDL remains in the bloodstream longer and may lead to the formation of plaque. Low HDL levels are seen in the people with diabetes. Both of these increase the risk of heart and artery disease. There is a link between high blood pressure (also called hypertension) and high cholesterol. When the arteries become narrowed and hardened with cholesterol plaque, the heart has to force much harder to pump blood through them. As a result, blood pressure becomes abruptly high.
Track 10: Cholesterol Metabolism
All the tissues synthesize cholesterol from acetyl-CoA. In adult the most actively synthesizing organs are liver and intestinal wall. The capacity of hydroxymethylglutarylCoA (HMG-CoA) reductase determines the rate of synthesis of cholesterol in most of the tissues. Cholesterol is absorbed in the presence of bile salts. After entering the cells of the intestinal mucosa, cholesterol is incorporated into chylomicrons, which enter the blood circulation via the lymphatic system. The proportion of the cholesterol in the food that is absorbed depends upon the intake of cholesterol and the amount of triglyceride in the diet; triglyceride tends to promote cholesterol absorption. It is then oxidized by the liver into a variety of bile acids. Bile acids, along with cholesterol itself, are excreted from the liver into the bile. Almost 95% of the bile acids are reabsorbed from the intestines, and the remainder are lost in the faeces. The excretion and reabsorption of bile acids forms the basis of the enterohepatic circulation.
Track 11: Cholesterol Metabolism and Diabetes
Cholesterol metabolism is altered in diabetes. Cholesterol absorption is decreased and the cholesterol biosynthesis is increased in diabetes. The increased cholesterol synthesis can be reduced by insulin. Low cholesterol absorption efficiency has been reported earlier in a limited number of diabetic subjects with mild hyperlipidemia and in moderately overweight. In type 2 diabetes, in obesity and in conditions such as cortisol excess (Cushing’s Syndrome), raised insulin levels are frequently found. Insulin resistance is often associated. Lack of insulin can lower the level of "good" cholesterol (HDL, or high density lipoprotein). When insulin is given and well controlled, HDL numbers typically go back to normal. Cholesterol problems in people who have type 1 diabetes are usually related to the lack of insulin. Gestation diabetes mellitus is associated with higher cholesterol synthesis in the first trimester, and elevated serum squalene levels in the second and third trimester of pregnancy, and that maternal serum squalene and cholesterol synthesis correlates with birth weight.
Track 12: Lipid Metabolism and Diabetes
Patients with diabetes often show abnormal lipid profiles because insulin regulates several of the steps of lipid metabolism. Patients with type 1 diabetes that exhibit effective glycaemic control may exhibit qualitative abnormalities. Dyslipidaemia in type2 diabetes is characterised by several strictly linked abnormalities: elevated fasting and postprandial triglycerides, a significant decrease in highâ€density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and an increase in smaller lowâ€density lipoprotein (LDL) and HDL particles. Also, the elevated postprandial triglycerides that are often present in patients with type2 diabetes may be linked to insulin resistance. Therefore, the abatement of hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance should be one of the main treatment objectives to address dyslipidaemia in patients with diabetes.
Track 13: Cardiovascular Diseases and Metabolic Risk
Presence of high level of cholesterol in the blood may increase risk of cardiovascular disease, heart attack and stroke. If the cholesterol is high, the excess oily substance will stick to the walls of the arteries, and eventually hardens, forming a type of plaque that damages the arteries. They become narrowed and lose their elasticity. This can contribute to the development of high blood pressure or hypertension, which can cause more damage to the blood vessels. The ultimate danger is that the arteries will become so narrowed that a blood clot will block blood flow, causing a severe cardiovascular event. Obesity, along with the high waist circumference and high body mass index, is an independent risk factor for coronary heart disease (CHD) and diabetes.
Track 14: Hypercholesterolemia and Hyperlipidaemia
Hyperlipidemia is the presence of high levels of fats (lipids) in the blood. The two major types of lipids found in the blood are cholesterol and triglycerides. Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is a medical term for abnormally high levels of cholesterol in the blood. Elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood may be an outcome of an unhealthy diet, obesity, inherited or the presence of other diseases such as type 2 diabetes. Hyperlipidemia has no symptoms, so the only way to detect it is to have your doctor perform a blood test called a lipid panel or a lipid profile. Lifestyle changes are the important aspect for managing hyperlipidemia. These changes alone may be enough to reduce the risk of complications like heart disease and stroke. Whereas hypercholesterolemia is typically due to a combination of environmental and genetic factors. Environmental factors include weight, diet, and stress. Familial hypercholesterolemia is a disorder that is passed down through families and caused by a defect on chromosome 19. It causes LDL (bad) cholesterol level to be very high. The condition begins at birth and can cause heart attacks at an early age.
Track 15: Recent Advances in Treatments and Therapies
Research activity in the field of diabetes has increased greatly in recent years and current standard of care for type 2 diabetes consists of screening for elevated HbA1c levels or, in some cases, fasting plasma glucose, with diagnosis followed by management with lifestyle modifications. People with type 2 diabetes can achieve their target blood sugar levels with diet, exercise and proper medications or insulin therapy. Insulin, along with diet, is crucial to the survival of individuals with type 1 diabetes. Pancreatic islet allo-transplantation is a procedure in which islets from the donor pancreas are transferred into another person to treat type 1 diabetes and have been a promising cellular-based therapy.
The artificial pancreas is a machine which would monitor blood glucose levels using an array of sensors, and release insulin from a reservoir into the bloodstream, using an infusion pump, whenever it is required. Current gene therapy study highlights the transfer of insulin gene into other cells such as the liver, stomach, or intestines. Bariatric surgery (weight loss surgery) is performed by reducing the size of the stomach with a gastric band or through removal of a portion of the stomach. The recent advances in nanomedicine include smart drugs which only activate when needed, nanoformulations for efficient drug delivery, engineered microbes which produce human hormones, and even nanorobots, which would move autonomously around the body acting as a boost, for our immune system, red blood cells, or many other biological systems.
“International Conference on Diabetes and Cholesterol Metabolism” is going to be held during October 15-17, 2018 in Dubai, UAE. The upcoming conference will be organized around the theme Be Stronger than Diabetes. This conference highlights the diabetes mellitus, diabetes complications, endocrinology, obesity, metabolic syndrome, epidemiology of diabetes, cholesterol metabolism, lipid metabolism, cardiovascular diseases, hypercholesterolemia, recent advances in treatments and therapies.
Metabolic Diseases 2018 Conference invites all renowned scientists, endocrinologists, surgeons, dieticians, radiation therapists, general physicians, primary health care specialists, epidemiologists, talented young scientists, pharmaceutical industrial delegates and student communities across the globe to attend International Metabolic Diseases conference under a single roof where investigators across the globe can meet, network, and perceive new scientific innovations.
Importance & scope
Diabetes is prevalent in all parts of the world. Number of people suffering from Diabetes disorders continues to rise each year. As reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), on an average 1 out of every 13 people are diagnosed globally with Diabetes each year and also projects that diabetes will be the 7th leading cause of death in 2030. Around 60% of the populations effected with Diabetes diseases are uncaring of the situation. The importance of both diabetes and their comorbidities will continue to increase as the population ages.
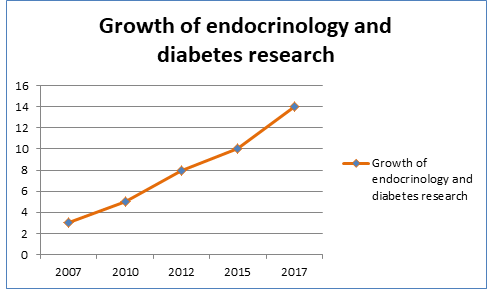
Metabolic Diseases 2018 will feature the latest developments in research, diagnosis, prevention and management of metabolic diseases, diabetes, new insulin analogues and new technologies, devices for diabetic prevention, for treating obesity and many more. Not only will this innovative conference enhance your practical and theoretical knowledge, it will provide you with the unique opportunity to network with a wide range of professionals in the field of diabetes technologies and treatments.
Societies Associated with Diabetes Research Worldwide
- Emirates Diabetes Society
- Global Health Partner Diabetes Centre Dubai
- Joslin Diabetes Centre Dubai
- Al Jalila Foundation Research Centre in Dubai
- Diabetes Research Institute Dubai
- Diabetes Education in Tribal Schools (DETS)
- International Diabetes Federation- Italy
- Australian Diabetes Society
- Immunology of Diabetes Society
- American Diabetes Association
- The Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes
- FAND - Italian Association of Diabetics
- Juvenile Diabetes Association
- Japan Diabetes Society
- Spanish Diabetes Society
- Korean Diabetes Association.
Universities which are dealing with Diabetic Research Worldwide:
- United Arab Emirates University
- University of Sharjah
- Imperial College London Diabetes Centre (UAE)
- New York University (UAE)
- Gulf medical university
- Harvard University (Cambridge, MA, USA),
- Columbia University (New York, NY, USA)
- Oxford University (Oxford, UK)
- Yale University (New Haven, CT, USA)
- McMaster University (Hamilton, ON, Canada)
- University of Strasbourg (Strasbourg, France)
Hospitals and Research Clinic which are dealing with Diabetic Research Worldwide:
- Cleveland Clinic Dubai
- Mayo clinic (Rochester, MN),
- Massachusetts General Hospital (Boston, MA)
- Cleveland Clinic (Cleveland, OH)
- Johns Hopkins Hospital (Baltimore, MD)
- Addenbrooke’s Hospital – Cambridge, Barnet General Hospital (UK)
- Cygnet Hospital Beckton (UK)
- Wooridul Spine Hospital-Seoul (South Korea)
- Fortis Memorial Research Institute (India)
Societies Associated with Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorders worldwide:
|
In terms of disease type, the diabetes drugs market has been classified into type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and impaired glucose tolerance and impaired fasting glycaemia. Type 2 diabetes has accounted for highest market share due to rising prevalence of obesity. Increasing physical inactivity created demand for the diabetes drugs. The prevalence of type 1 diabetes made type 1 diabetes to hold the second large market share in 2016. Due to the high prevalence of diabetes in the relatives and heredity reason, gestational diabetes, impaired glucose tolerance, and impaired fasting glycaemia are expected to grow during the forecast period 2017 to 2025.
Why Dubai?
Dubai is the largest city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). It is extremely well known for its warm hospitality, rich cultural heritage, futuristic architecture, luxury shopping and the Emirati people are welcoming and munificent in their approach to visitors. Dubai is a destination that mixes modern culture with history, entertainment with world-class shopping and adventure. Glitzy Dubai is the United Arab Emirates holiday hot spot. This city of high-rises and shopping malls has transformed itself from a desert outpost to a destination where tourists flock for sales, sunshine and family fun. Dubai is famous for sightseeing such as Burj Khalifa (a mega tall skyscraper), mammoth aquariums and that come complete with Dubai museum and indoor ski slopes.
The United Arab Emirates (U.A.E.) is actively increasing its healthcare system to support economic diversification and to satisfy the needs of its people, with leading U.S. corporations. There are four regulators in the UAE: - The Ministry of Health - Dubai Healthcare City Free Zone - Dubai Health Authority (DHA) - Health Authority Abu Dhabi (HAAD). The UAE’s 2021 Vision states that “the UAE will invest continually to build world-class healthcare infrastructure, expertise and services in order to fulfil citizens’ growing needs and expectations.” Dubai attracted 260,000 medical tourists in the first half of 2015, up 12% from the same period a year ago. By 2020, the Dubai Health Authority aims to grow the number of medical tourists by around 12% annually and to generate Dh2.6 billion in revenue.
Related Conferences:
Global Experts Meeting On Diabetes, Hypertension & Metabolic Syndrome July 30-31, 2018 Melbourne, Australia; Global Meeting on Diabetes and Endocrinology July 25-26, 2018 Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia; International Conference on Diabetes and its Complications May 28-29, 2018 Osaka, Japan; 24th International Conference on Herbal and Alternative Therapies for Diabetes August 17-18, 2018 Singapore; 25th Global Summit on Human Metabolic Health- Diabetes, Obesity, & Metabolism September 6-8, 2018 Dubai, UAE; 11th International Conference on Endocrinology & Endocrine Disorder October 17-18, 2018 Las Vegas, USA; 12th International Conference on Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism October 01-02, 2018 Osaka, Japan
Related societies:
Middle East Countries: Emirates Diabetes Society | Global Health Partner Diabetes Centre | Joslin Diabetes Centre | Al Jalila Foundation Research Centre | Diabetes Research Institute | Diabetes Education in Tribal Schools (DETS) | Syria Diabetes Association | Israel Diabetes Association | Turkish Diabetes Association | Saudi Diabetes & Endocrine Association | The Egyptian Union of Diabetes Association | Lebanese Diabetes Association | Bahrain Diabetic Association | Cyprus Diabetes Association
USA: American Association of Diabetes Educators | American Diabetes Association | Canadian Diabetes Association | American Association for Clinical Endocrinology | Diabetes Canada
Europe: European Society of Endocrinology | Central European Diabetes Association | FAND - Italian Association of Diabetics | Italian Association for the Defence of the Interests of Diabetics | International Diabetes Federation- Italy | German Diabetes Union | Franquise Association of Diabetics | British Diabetes Association | Spanish Diabetic Society | Hellenic Diabetologic Association | Swiss Diabetes Association | Dutch Diabetes Association | Polish Diabetes Association | Austrian Diabetics Association | Swedish Diabetic Association | Norwegian Diabetes Association | Maltese Diabetes Association | Czech Diabetes Society | Society of Diabetes, Nutrition & Metabolic Diseases | Hungarian Diabetes Association | Bulgarian Diabetes Association | Cyprus Diabetes Association | Finnish Diabetes Association | Albania Diabetes Association | Lithuania Diabetes Association | Estonia Diabetes Association
Asia-Pacific: Australian Diabetes Society | Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes | Diabetes Association of Nigeria | Diabetes Association of the Republic of China | Asian Diabetic Association | Diabetes Society of the Chinese Medical Association | Diabetic Association of India | Japan Diabetes Society | Korean Diabetes Association | Indonesian Diabetes Association | Diabetes Association of Thailand | Malaysia Diabetes Association | Diabetic Society of Singapore | Philippine Diabetes Association | Diabetic Association of Bangladesh | Diabetes New Zealand | Diabetes Association of Sri Lanka
Euro Diabetes 2017
Thanks to all our momentous speakers, delegates, and all the conference attendees contributed for the success of 18th European Diabetes Congress (Euro Diabetes 2017) convoked by ME Conferences during July 17-18, 2017 was successfully held at Embassy suites Lisbon, Portugal with a theme “Diabetes Explosion: Developments and Changing Life of Diabetes World” was a great success where eminent keynote speakers from various reputed institutions with their resplendent presence addressed the gathering.
Euro Diabetes 2017 witnessed an amalgamation of peerless speakers who enlightened the crowd with their knowledge and confabulated on various new-fangled topics related to the fields of Endocrinology, Diabetes, Pediatrics, and Surgery.
The meeting was carried out through various sessions, in which the discussions were held on the following major scientific tracks:
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetes Chronic Complication
- Biomarkers for Diabetes
- Diabetes Research
- Treatment Of Diabetes
- Insulin Medication
- Type 2 diabetes & Obesity
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Biology of Diabetes
- Transplantation/ Immunology
- Genetics of Diabetes
- Diabetes Medication & Therapy
Euro Diabetes 2017 Organizing Committee would like to thank the Moderators of the conference, Ualikhanova A, RUDN University, Russia and Sherry Elisha Mata, Cairo University, Egypt who has contributed a lot for the smooth functioning of this event.
Euro Diabetes 2017 extends its warm gratitude to all the Honourable Guest and Keynote Speakers of the event:
- Dr. Palayakotai Raghavan, CEO of Nanorx INC; USA.
- Dr. Arturo Solis Herrera; Director and Founder of Human Photosynthesis® Research Center, Mexico
- Dr. Nandakumaran Moorkath, professor at University of Kuwait, Kuwait.
- Dr. Irina Kurnikova, Professor of Medicine in RUDN University, Russia.
ME conferences is privileged to felicitate Euro Diabetes 2017 Organizing Committee, Chairs & Co-Chairs who supported for the success of this event. ME conferences would like to thank every individual participant for the enormous exquisite response. This inspires us to continue organizing events and conferences for further research in the field of Diabetes.
With the valuable feedback received from the participants of Euro Diabetes 2017, Conference Series LLC is glad to announce the commencement of “International Conference on Diabetes and Cholesterol Metabolism” during October 15-17, 2018 at Dubai, UAE. We welcome all the eminent researchers, students and delegate participants to take part in this upcoming conference to witness invaluable scientific discussions and contribute to the future innovations in the field of managing diabetes and its concomitant risk factors.
Conference Highlights
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Gestational Diabetes
- Diabetes Complications
- Endocrinology
- Diabetes and Obesity
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Epidemiology of Diabetes
- Diabetic Education and Healthcare Professionals
- Cholesterol, High Blood Pressure and Diabetes
- Cholesterol Metabolism
- Cholesterol Metabolism and Diabetes
- Lipid Metabolism and Diabetes
- Cardiovascular Diseases and Metabolic Risk
- Hypercholesterolemia and Hyperlipidaemia
- Recent Advances in Treatments and Therapies
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 15-17, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Diabetes & Metabolism
- Journal of Metabolic Syndrome
- Journal of Diabetic Complications & Medicine
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by